Table of Contents
- Pre-requisites & Setup
- What is Ansible
async? - Waiting for your asynchronous task with
async_status - Ansible Asynchronous Ad-Hoc Tasks
- Can you use Ansible async with
blockORinclude_tasks? - How to wait / check on multiple async tasks with async_status
- async & async_status with
loopsandwith_items - Scenario: Restart a host and wait for reboot to complete
- Scenario: retry
asynctask inside block after resuce task - Conclusion
In this guide we will look at how we can run parallel and asynchronous tasks within your playbooks in order to run your playbook in the most efficient way possible!
This post is a more detailed version of this article about using Ansible’s
asyncto run your tasks in parallel.
Pre-requisites & Setup
- I’m using
ansible-core 2.14 - Ansible Host is running Python 3 on Ubuntu
- Managed/remote host(s) is running Python 2.7 on Ubuntu
What is Ansible async?
By default, a playbook’s task are ran synchronously meaning that a task must be completed before moving onto the next task.
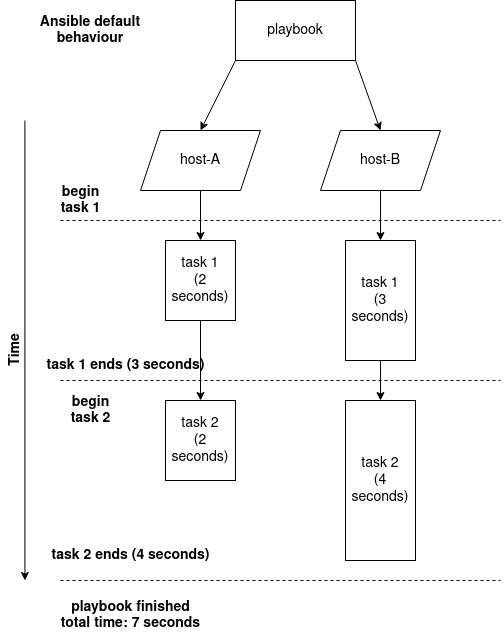
Ansible default behavior: Whilst tasks as ran concurrently amongst multiple target hosts, tasks are still executed synchronously
There are at least 2 problems with Ansible’s default synchronous behavior:
- A long-running task may cause Ansible’s connection to the host (SSH) to timeout
- You may want your long-running task to run in the background whilst the rest of your tasks are carried out (efficient execution)
Ansible solves these 2 problems by introducing the use of the async and poll keyword.
| async | sets the timeout of the task |
| poll | how often Ansible should poll the task for its status |
How to handle long-running tasks (prevent timeout)
You can use async and a poll value greater than 0 in order to keep your long-running tasks running without a getting stopped due to connection timeout.
In this example - Setting async: 30 means that the task will wait up to 30 seconds for the task to be completed (if not, it will result in a timeout). And poll: 2 means that Ansible will poll for task status every 2 seconds.
Example
- hosts: docker-server
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- name: task 1 - run for 10s, wait up to 30s, poll for status every 2s
ansible.builtin.command: sleep 10
async: 30
poll: 2
Output (Click to show)
TASK [task 1] ***************************************************************************************************************
Monday 17 July 2023 17:24:01 +0000 (0:00:00.024) 0:00:00.024 ***********
ASYNC POLL on docker-server: jid=j999005543702.10594 started=1 finished=0
ASYNC POLL on docker-server: jid=j999005543702.10594 started=1 finished=0
ASYNC POLL on docker-server: jid=j999005543702.10594 started=1 finished=0
ASYNC POLL on docker-server: jid=j999005543702.10594 started=1 finished=0
ASYNC OK on docker-server: jid=j999005543702.10594
changed: [docker-server]
PLAY RECAP ******************************************************************************************************************
docker-server : ok=1 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Monday 17 July 2023 17:24:12 +0000 (0:00:11.482) 0:00:11.506 ***********
===============================================================================
task 1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 11.48sIn the output, you can see that because the task only runs for 10 seconds and is polled every 2 seconds, it only got polled 5 times before finally completing.
In this example, our task still blocks other tasks from running, but it won’t time out as we have increase the timeout to an amount that we want.
Running your tasks in parallel - poll = 0
If you want to run 2 or more different tasks in your playbook in parallel, then set poll: 0. Ansible will run the task and immediately move onto the next task. Tasks will run until the timeout value (async value) is reached or if the task either fails/completes.
It’s important to note that Ansible will fire-and-forget your task meaning if you don’t have any synchronous task after, The playbook will exit (more on this in Example 1).
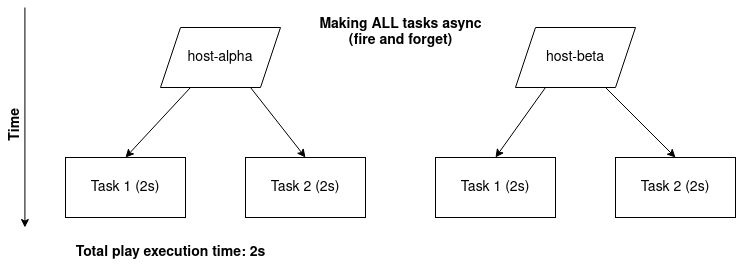
Example 1 - 1 async task only (poll = 0)
In this example, you will see that task 1 (sleep for 5 seconds) will run and then immediately the playbook will end (Ansible does not wait 5 seconds before the playbook ends).
This is because with poll: 0 Ansible just executes the task and forgets about it. Ansible WILL NOT check on the task’s status.
- hosts: docker-server
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- name: task 1
ansible.builtin.command: sleep 5
async: 10
poll: 0
Output (Click to show)
TASK [task 1] **********************************************************************************************************************
Monday 17 July 2023 20:08:25 +0000 (0:00:00.016) 0:00:00.016 ***********
changed: [docker-server]
PLAY RECAP *************************************************************************************************************************
docker-server : ok=1 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Monday 17 July 2023 20:08:25 +0000 (0:00:00.494) 0:00:00.510 ***********
===============================================================================
task 1 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.49sExample 2 - running your task whilst other tasks are running
In this example we have an async task (sleep 5s) which is executed and immediately Ansible will move onto the next task which prints the output of the async task.
- hosts: docker-server
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- name: task 1
ansible.builtin.command: /bin/sleep 5
async: 5
poll: 0
register: job_res
- name: output async task 1
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "{{job_res}}"
Output (Click to show)
TASK [task 1] **********************************************************************************************************************
Monday 17 July 2023 20:18:34 +0000 (0:00:00.016) 0:00:00.016 ***********
changed: [docker-server]
TASK [output async task 1] *********************************************************************************************************
Monday 17 July 2023 20:18:34 +0000 (0:00:00.832) 0:00:00.849 ***********
ok: [docker-server] => {
"msg": {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3"
},
"ansible_job_id": "j388948066885.44169",
"changed": true,
"failed": 0,
"finished": 0,
"results_file": "/home/user/.ansible_async/j388948066885.44169",
"started": 1
}
}
PLAY RECAP *************************************************************************************************************************
docker-server : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Monday 17 July 2023 20:18:34 +0000 (0:00:00.092) 0:00:00.941 ***********
===============================================================================
task 1 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.83s
output async task 1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.09sIn the output, we print the result of the async task which is:
TASK [output async task 1] *********************************************************************************************************
Monday 17 July 2023 20:18:34 +0000 (0:00:00.832) 0:00:00.849 ***********
ok: [docker-server] => {
"msg": {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3"
},
"ansible_job_id": "j388948066885.44169",
"changed": true,
"failed": 0,
"finished": 0,
"results_file": "/home/user/.ansible_async/j388948066885.44169",
"started": 1
}
}
You can see that the task was started: 1 and changed: true, but it was not finished. Ansible executed the async task but did not check on whether it finished.
Sometimes, you might have use case for this behavior, but most of the time you will want to check on the outcome of your async task - You can achieve this using async_status - More on this in the next section.
Waiting for your asynchronous task with async_status
Quite often you may run into a use case where:
- You want to run a task in the background (async task)
- Whilst running some other tasks sequentially
- But you want to finish your async task before moving on with the rest of the playbook
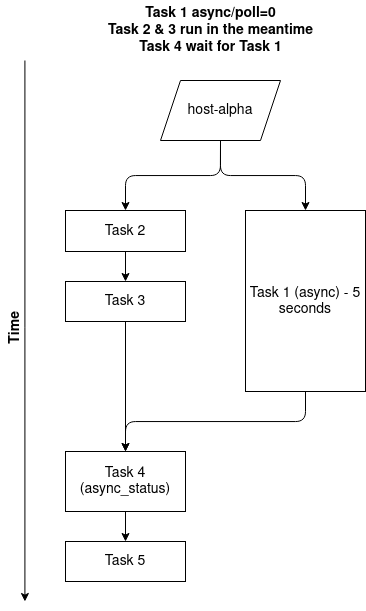
You can use Ansible async_status to check on your async task status to ensure that it is finished.
Example - Using async_status and until to wait for your async task
In order to wait for your async task you need to use async_status to check for the async task’s status and the until keyword to wait until the async task’s status has changed to the status you want.
- hosts: docker-server
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- name: task 1 - background task
ansible.builtin.command: /bin/sleep 5
async: 10
poll: 0
register: async_task_result
- name: task 2
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: task 2
- name: task 3
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: task 3
- name: Task 4 - wait for async task
ansible.builtin.async_status:
jid: "{{ async_task_result.ansible_job_id }}"
until: job_result.finished
register: job_result
retries: 10
delay: 2
- name: task 5
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: task 4
Output (Click to show)
TASK [task 1 - background task] ****************************************************************************************************
Wednesday 19 July 2023 19:02:58 +0000 (0:00:00.015) 0:00:00.015 ********
changed: [docker-server]
TASK [task 2] **********************************************************************************************************************
Wednesday 19 July 2023 19:02:58 +0000 (0:00:00.585) 0:00:00.600 ********
ok: [docker-server] => {
"msg": "task 2"
}
TASK [task 3] **********************************************************************************************************************
Wednesday 19 July 2023 19:02:58 +0000 (0:00:00.080) 0:00:00.681 ********
ok: [docker-server] => {
"msg": "task 3"
}
TASK [Task 4 - wait for async task] ************************************************************************************************
Wednesday 19 July 2023 19:02:58 +0000 (0:00:00.031) 0:00:00.712 ********
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: Task 4 - wait for async task (10 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: Task 4 - wait for async task (9 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: Task 4 - wait for async task (8 retries left).
changed: [docker-server]
TASK [task 5] **********************************************************************************************************************
Wednesday 19 July 2023 19:03:05 +0000 (0:00:06.906) 0:00:07.619 ********
ok: [docker-server] => {
"msg": "task 4"
}
PLAY RECAP *************************************************************************************************************************
docker-server : ok=5 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Wednesday 19 July 2023 19:03:05 +0000 (0:00:00.031) 0:00:07.651 ********
===============================================================================
Task 4 - wait for async task ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 6.91s
task 1 - background task ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.59s
task 2 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.08s
task 5 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.03s
task 3 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.03sExplanation
- task 1 is run asynchronously (supposed to be a 5-second task)
- task 2 and then 3 ran immediately after task 1
- task 4 keeps checking if the async task is finished
- once task 4 confirms that task 1 is finished, it moved to task 5
- you will see that task 4 (wait for async task) retried 3 times until the async task was finally completed
register: job_result- this is the result of the async_status check. This will give us an async task’s status objectuntil: job_result.finished- runs the async_status task until the job result of the async task is finished=1 (or async task is finished)retries: 10anddelay: 2, just means keep trying the async_status every 2 second, with a maximum of 10 retries until the condition is met or the retry count is breached
Note if you don’t set
retries, it will default to 3
Why can’t you just check async_task_result directly without using async_status?
You can see on Task 1 (async task) that we do register: async_task_result. If we try to access async_task_result we will get the async task’s status object, but it will not be updated so the until condition will never be met.
See this Wrong example where we try to wait for the async task to finish:
- name: task 1 - background task
ansible.builtin.command: /bin/sleep 5
async: 10
poll: 0
register: async_task_result
- name: task 2
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "{{async_task_result}}"
until: async_task_result.finished
retries: 5
delay: 2
See the output error, the printing the result of the async_task_result object shows that we never detected the async task finishing. It finally throws an error from trying 5 times and still not meeting the condition: until: async_task_result.finished:
TASK [task 1 - background task] ****************************************************************************************************
Wednesday 19 July 2023 19:22:29 +0000 (0:00:00.014) 0:00:00.014 ********
changed: [docker-server]
TASK [task 2] **********************************************************************************************************************
Wednesday 19 July 2023 19:22:29 +0000 (0:00:00.778) 0:00:00.793 ********
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: task 2 (5 retries left).Result was: {
"attempts": 1,
"changed": false,
"msg": {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3"
},
"ansible_job_id": "j450847278915.82341",
"changed": true,
"failed": 0,
"finished": 0,
"results_file": "/home/user/.ansible_async/j450847278915.82341",
"started": 1
},
"retries": 6
}
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: task 2 (4 retries left).Result was: {
"attempts": 2,
"changed": false,
"msg": {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3"
},
"ansible_job_id": "j450847278915.82341",
"changed": true,
"failed": 0,
"finished": 0,
"results_file": "/home/user/.ansible_async/j450847278915.82341",
"started": 1
},
"retries": 6
}
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: task 2 (3 retries left).Result was: {
"attempts": 3,
"changed": false,
"msg": {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3"
},
"ansible_job_id": "j450847278915.82341",
"changed": true,
"failed": 0,
"finished": 0,
"results_file": "/home/user/.ansible_async/j450847278915.82341",
"started": 1
},
"retries": 6
}
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: task 2 (2 retries left).Result was: {
"attempts": 4,
"changed": false,
"msg": {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3"
},
"ansible_job_id": "j450847278915.82341",
"changed": true,
"failed": 0,
"finished": 0,
"results_file": "/home/user/.ansible_async/j450847278915.82341",
"started": 1
},
"retries": 6
}
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: task 2 (1 retries left).Result was: {
"attempts": 5,
"changed": false,
"msg": {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3"
},
"ansible_job_id": "j450847278915.82341",
"changed": true,
"failed": 0,
"finished": 0,
"results_file": "/home/user/.ansible_async/j450847278915.82341",
"started": 1
},
"retries": 6
}
fatal: [docker-server]: FAILED! => {
"msg": {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3"
},
"ansible_job_id": "j450847278915.82341",
"changed": true,
"failed": 0,
"finished": 0,
"results_file": "/home/user/.ansible_async/j450847278915.82341",
"started": 1
}
}
PLAY RECAP *************************************************************************************************************************
docker-server : ok=1 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=1 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Wednesday 19 July 2023 19:22:40 +0000 (0:00:10.078) 0:00:10.872 ********
===============================================================================
task 2 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 10.08s
task 1 - background task ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.78s
Run your task in the background (even after playbook finishes)
An Ansible fire-and-forget async task will still keep running in the background when the async task is incomplete and the playbook has already finished!
To test this, I create 2 playbooks:
- Playbook 1 will run an async task (sleep 15s) and print the
ansible_job_id - We will quickly edit playbook 2 (Whilst the async task is still running in the background) to check the
async_statusof the async task from playbook 1 (We will manually hard-code theansible_job_idprinted from playbook 1)
Part 1 - Run Playbook 1 - fire async task
Playbook 1 - runs a 15 second async task and then immediately prints the ansible_job_id which is - “j965205278735.13393”
- name: task 1 - background task
ansible.builtin.command: /bin/sleep 15
async: 100
poll: 0
register: async_task_result
- name: task 3
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "{{ async_task_result.ansible_job_id }}"
Output - you can see that the async task’s job id is “j965205278735.13393”
TASK [task 1 - background task] ****************************************************************************************************
Wednesday 19 July 2023 21:18:39 +0000 (0:00:00.025) 0:00:00.025 ********
changed: [docker-server]
TASK [task 3] **********************************************************************************************************************
Wednesday 19 July 2023 21:18:39 +0000 (0:00:00.577) 0:00:00.603 ********
ok: [docker-server] => {
"msg": "j965205278735.13393"
}
PLAY RECAP *************************************************************************************************************************
docker-server : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Wednesday 19 July 2023 21:18:39 +0000 (0:00:00.090) 0:00:00.693 ********
===============================================================================
task 1 - background task ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.58s
task 3 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.09s
Part 2 - Run playbook 2 - Get async_status of async task from Playbook 1
We set the job id (jid) to “j965205278735.13393” based on the async task’s Job ID printed from Playbook 1.
- name: wait for async task executed from another playbook
ansible.builtin.async_status:
jid: "j965205278735.13393" # <-- have to add this quickly before async task ends
until: job_result.finished
register: job_result
retries: 10
delay: 3
- name: finished waiting
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "Finished waiting for async task"
The output - You can see that async_status waited for the async task to finish before doing the last task.
TASK [wait for async task executed from another playbook] **************************************************************************
Wednesday 19 July 2023 21:18:49 +0000 (0:00:00.014) 0:00:00.014 ********
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async task executed from another playbook (10 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async task executed from another playbook (9 retries left).
changed: [docker-server]
TASK [finished waiting] ************************************************************************************************************
Wednesday 19 July 2023 21:18:56 +0000 (0:00:06.821) 0:00:06.835 ********
ok: [docker-server] => {
"msg": "Finished waiting for async task"
}
PLAY RECAP *************************************************************************************************************************
docker-server : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Wednesday 19 July 2023 21:18:56 +0000 (0:00:00.031) 0:00:06.867 ********
===============================================================================
wait for async task executed from another playbook -------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6.82s
finished waiting ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 0.03s
This proves that your incomplete async fire-and-forget tasks will still run even after the playbook finishes.
Clearing any incomplete async tasks
If you want to make sure that there are no incomplete async tasks run in the background when your playbook finishes, you can do:
ansible.builtin.async_status:
jid: "{{ the ansible_job_id value }}"
mode: cleanup
As shown in this example:
- we run and async task
- we clean up the async job cache
- we try to wait for the async task but we will fail since the async job has been cleared
- name: task 1 - background task
ansible.builtin.command: /bin/sleep 25
async: 100
poll: 0
register: async_task_result
- name: Cleanup async task
ansible.builtin.async_status:
jid: "{{ async_task_result.ansible_job_id }}"
mode: cleanup
- name: Wait for async task
ansible.builtin.async_status:
jid: "{{ async_task_result.ansible_job_id }}"
until: job_result.finished
register: job_result
retries: 10
delay: 3
The output, is that once we get to the 3rd task (“wait for async task”) it will fail since the async task no longer exists (because the async job cahce has been cleared):
TASK [task 1 - background task] ****************************************************************************************************
Wednesday 19 July 2023 21:41:47 +0000 (0:00:00.019) 0:00:00.019 ********
changed: [docker-server]
TASK [Cleanup async task] **********************************************************************************************************
Wednesday 19 July 2023 21:41:47 +0000 (0:00:00.451) 0:00:00.471 ********
ok: [docker-server]
TASK [Task 4 - wait for async task] ************************************************************************************************
Wednesday 19 July 2023 21:41:48 +0000 (0:00:00.389) 0:00:00.860 ********
fatal: [docker-server]: FAILED! => {"ansible_job_id": "j177433000798.18284", "attempts": 1, "changed": false, "finished": 1, "msg": "could not find job", "results_file": "/home/user/.ansible_async/j177433000798.18284", "started": 1, "stderr": "", "stderr_lines": [], "stdout": "", "stdout_lines": []}
PLAY RECAP *************************************************************************************************************************
docker-server : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=1 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Wednesday 19 July 2023 21:41:48 +0000 (0:00:00.178) 0:00:01.039 ********
===============================================================================
task 1 - background task ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.45s
Cleanup async task ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.39s
Wait for async task ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 0.18s
Ansible Asynchronous Ad-Hoc Tasks
You can use async with Ansible’s Ad-Hoc commands to run your ad-hoc tasks in the background.
Set the timeout using -B (seconds) and the polling rate with -P (seconds).
Here in this example, we target the host docker-server, with a timeout of 15 seconds and poll to 0 (So it will fire-and-forget the task)
ansible docker-server -B 15 -P 0 -m "ansible.builtin.command" -a "sleep 10"
This will output:
docker-server | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3"
},
"ansible_job_id": "j357149237731.7386",
"changed": true,
"finished": 0,
"results_file": "/home/user/.ansible_async/j357149237731.7386",
"started": 1
}
After 10 seconds (because we use sleep 10), we do another ad-hoc command to check the async_status of the async task we just set:
ansible docker-server -m async_status -a "jid=j357149237731.7386"
The output being:
docker-server | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python3"
},
"ansible_job_id": "j357149237731.7386",
"changed": true,
"cmd": [
"sleep",
"10"
],
"delta": "0:00:10.005101",
"end": "2023-07-19 21:59:44.172199",
"finished": 1,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results_file": "/home/user/.ansible_async/j357149237731.7386",
"start": "2023-07-19 21:59:34.167098",
"started": 1,
"stderr": "",
"stderr_lines": [],
"stdout": "",
"stdout_lines": []
}
Can you use Ansible async with block OR include_tasks?
async + block
No. You cannot use async with ansible blocks, BUT you can use async inside ansible block.
❌ WRONG - blocks with async
- block:
- ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: sleep 20
async: 50
poll: 2
✅ CORRECT - async inside block
- block:
- ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: sleep 20
async: 50
poll: 2
async + include_tasks
No. Similar with blocks, you cannot use async with include_tasks but you can use async inside the included task.
You cannot use async with “pay modifying directives” (like include_role etc. etc.) as mentioned in this ansible github issue
❌ WRONG - include_task with async
- ansible.builtin.include_tasks:
file: ./some-task.yml
async: 20
poll: 0
✅ CORRECT - async inside the included task
# main task
- ansible.builtin.include_tasks:
file: ./some-task.yml
# included task
- ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: sleep 20
async: 50
poll: 2
How to run blocks of tasks in parallel in Ansible
If you want to run multiple segments of tasks using blocks/include_tasks in parallel you need to re-consider your design since you cannot use async with blocks / include_tasks.
But there is a way…
The solution
Let’s say you have this scenario that you want to implement:
- Task 1 is a block of 2 tasks
- Task 2 is a block of 2 tasks
- Task 3 is just a single task
- You want to run Task 1, 2 and 3 concurrently
- Once all 3 tasks are finished, move onto task 4
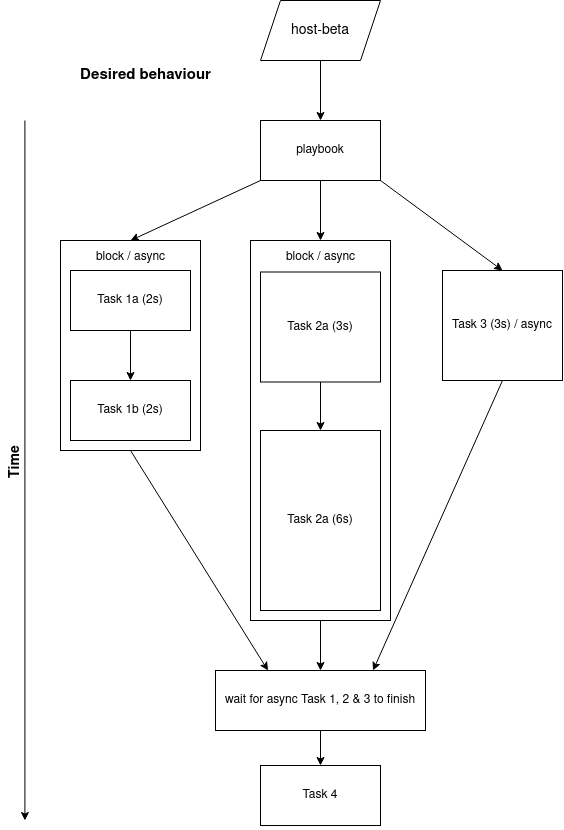
There is no straight forward way to solve this, And often times it is a better way to solve this is tailor your playbook to what is within Ansible’s capabilities.
Here’s my solution ✅:
- Remove the use of
block(orinclude_tasks) - Run Task 1a, 2a and 3 in parallel (async / poll = 0)
- Wait for those 3 tasks to finish using
async_status - Run Task 1b and in parallel (async / poll = 0)
- Wait for these 2 tasks to finish using
async_status - Run Task 4
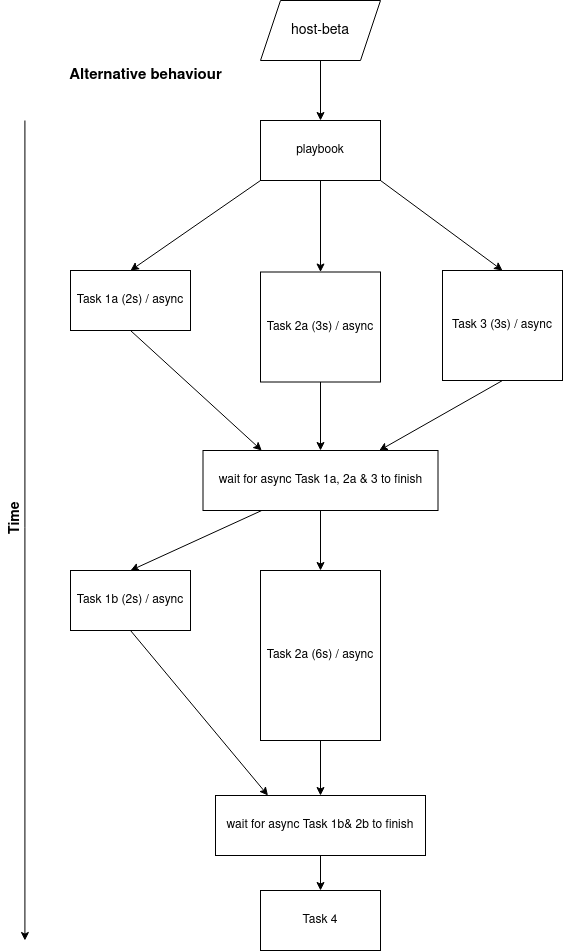
This way we:
- still keep the order of all task’s execution
- whilst still being able to run different tasks in parallel.
NOTE: Another problem you might run into is how do you wait for multiple async tasks with only ONE async_status task? We talk about this in the sections below!
NOTE: If you just want to run multiple different playbooks in parallel then check out this example this example using the
ansible-parallelpackage to execute multiple playbooks in parallel.
How to wait / check on multiple async tasks with async_status
What if you want to wait for or check on the status of multiple async tasks?
- hosts: docker-server
tasks:
- name: Task 1
ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: sleep 5
async: 30
poll: 0
register: t1
- name: Task 2
ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: sleep 10
async: 30
poll: 0
register: t2
- name: wait for async task 1 & 2 before doing task 3
ansible.builtin.async_status:
jid: "{{ item.ansible_job_id }}"
register: job
until: job.finished
retries: 10
delay: 1
with_items: "{{ [t1, t2] }}"
- name: Task 3
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: Last Task
NOTE: If you created multiple async tasks using loop/with_items, then you need to access the “results” key of the registered variable - more info on the next section
Explanation:
- Task 1 (5 seconds) and Task 2 (10 seconds) is executed concurrently
- The output of task 1 is
t1and for task 2 itst2 - We use
with_itemsto loop through t1 and t2’s (task 1 & 2’s results) and check their task status - We wait until BOTH t1 and t2 are finished
- After that, we move to Task 3
In the output, you can see that task 1 finished first and task 2 finished after
Output (Click to show)
TASK [Gathering Facts] *************************************************************************************************************
Saturday 22 July 2023 15:04:23 +0000 (0:00:00.014) 0:00:00.014 *********
ok: [docker-server]
TASK [Task 1] **********************************************************************************************************************
Saturday 22 July 2023 15:04:24 +0000 (0:00:01.328) 0:00:01.343 *********
changed: [docker-server]
TASK [Task 2] **********************************************************************************************************************
Saturday 22 July 2023 15:04:25 +0000 (0:00:00.488) 0:00:01.832 *********
changed: [docker-server]
TASK [wait for async task 1 & 2 before doing task 3] *******************************************************************************
Saturday 22 July 2023 15:04:25 +0000 (0:00:00.384) 0:00:02.217 *********
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async task 1 & 2 before doing task 3 (10 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async task 1 & 2 before doing task 3 (9 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async task 1 & 2 before doing task 3 (8 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async task 1 & 2 before doing task 3 (7 retries left).
changed: [docker-server] => (item={'failed': 0, 'started': 1, 'finished': 0, 'ansible_job_id': 'j202090433164.58721', 'results_file': '/home/user/.ansible_async/j202090433164.58721', 'changed': True})
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async task 1 & 2 before doing task 3 (10 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async task 1 & 2 before doing task 3 (9 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async task 1 & 2 before doing task 3 (8 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async task 1 & 2 before doing task 3 (7 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async task 1 & 2 before doing task 3 (6 retries left).
changed: [docker-server] => (item={'failed': 0, 'started': 1, 'finished': 0, 'ansible_job_id': 'j581718129529.58764', 'results_file': '/home/user/.ansible_async/j581718129529.58764', 'changed': True})
TASK [Task 3] **********************************************************************************************************************
Saturday 22 July 2023 15:04:36 +0000 (0:00:11.122) 0:00:13.340 *********
ok: [docker-server] => {
"msg": "Last Task"
}
PLAY RECAP *************************************************************************************************************************
docker-server : ok=5 changed=3 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Saturday 22 July 2023 15:04:36 +0000 (0:00:00.062) 0:00:13.402 *********
===============================================================================
wait for async task 1 & 2 before doing task 3 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 11.12s
Gathering Facts ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1.33s
Task 1 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.49s
Task 2 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.38s
Task 3 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.06sasync & async_status with loops and with_items
You can also use async with loop and with_items for a more dynamic playbook flow. For example, you might have a list of download links, and you want your playbook to initiate a download task for all the links.
Example - loops / with_items with async + wait for all downloads to finish
In this example, we sleep fire-and-forget 4 async tasks (sleep 1 to 4 seconds). And wait for all of them to finish.
This example also shows how you can register the result of a “looped” task
- hosts: docker-server
vars:
sleep_times:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
tasks:
- ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: "sleep {{ item }}"
async: 10
poll: 0
loop: "{{ sleep_times }}"
register: async_result
- name: wait for async tasks
ansible.builtin.async_status:
jid: "{{ item.ansible_job_id }}"
register: job_status
until: job_status.finished
with_items: "{{ async_result.results }}"
retries: 30
delay: 1
- name: Task finish
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: Playbook Finished
Output (Click to show)
TASK [Gathering Facts] *************************************************************************************************************
Sunday 23 July 2023 18:31:39 +0000 (0:00:00.019) 0:00:00.019 ***********
ok: [docker-server]
TASK [ansible.builtin.command] *****************************************************************************************************
Sunday 23 July 2023 18:31:40 +0000 (0:00:01.421) 0:00:01.440 ***********
changed: [docker-server] => (item=1)
changed: [docker-server] => (item=2)
changed: [docker-server] => (item=3)
changed: [docker-server] => (item=4)
TASK [wait for async tasks] ********************************************************************************************************
Sunday 23 July 2023 18:31:41 +0000 (0:00:01.351) 0:00:02.791 ***********
changed: [docker-server] => (item={'failed': 0, 'started': 1, 'finished': 0, 'ansible_job_id': 'j721147755818.9559', 'results_file': '/home/user/.ansible_async/j721147755818.9559', 'changed': True, 'item': 1, 'ansible_loop_var': 'item'})
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (30 retries left).
changed: [docker-server] => (item={'failed': 0, 'started': 1, 'finished': 0, 'ansible_job_id': 'j730084032155.9600', 'results_file': '/home/user/.ansible_async/j730084032155.9600', 'changed': True, 'item': 2, 'ansible_loop_var': 'item'})
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (30 retries left).
changed: [docker-server] => (item={'failed': 0, 'started': 1, 'finished': 0, 'ansible_job_id': 'j551273134437.9640', 'results_file': '/home/user/.ansible_async/j551273134437.9640', 'changed': True, 'item': 3, 'ansible_loop_var': 'item'})
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (30 retries left).
changed: [docker-server] => (item={'failed': 0, 'started': 1, 'finished': 0, 'ansible_job_id': 'j945902683231.9681', 'results_file': '/home/user/.ansible_async/j945902683231.9681', 'changed': True, 'item': 4, 'ansible_loop_var': 'item'})
TASK [Task finish] *****************************************************************************************************************
Sunday 23 July 2023 18:31:46 +0000 (0:00:04.337) 0:00:07.129 ***********
ok: [docker-server] => {
"msg": "Playbook Finished"
}
PLAY RECAP *************************************************************************************************************************
docker-server : ok=4 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Sunday 23 July 2023 18:31:46 +0000 (0:00:00.061) 0:00:07.190 ***********
===============================================================================
wait for async tasks -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 4.34s
Gathering Facts ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1.42s
ansible.builtin.command ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1.35s
Task finish ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.06sExplanation
- We have a list variable
sleep_timeswhich we will use to define the time value of the sleep command - we loop through
sleep_timesto quickly fire-and-forget 4 async tasks (sleep 1s, sleep 2s, sleep 3s, sleep 4s) - we register the output of the async task into a variable called
async_result - To access the
async_resultfor each async task, we loop through the “results” key bywith_items: "" async_statuswill wait until the async task is finished (it will check 30 times with an interval of 1 second between each check)
Run async task in batches (limit concurrent async tasks)
You may run into a scenario where you have to limit the amount of async tasks running simultaneously e.g. you may be limited to 3 downloads of a URL, per host.
So you want to run your async tasks in batches of 3, wait for the async tasks to finish then move onto the next batch of 3 and so on.
NOTE: If you want to further limit how many hosts can run simultaneously, you can use the Ansible
throttleor Ansibleforks
# main.yml
- hosts: docker-server
vars:
sleep_times:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
tasks:
- name: Run in batches of 3
vars:
batched_sleep_times: "{{ item }}"
include_tasks: batch-task.yml
loop: "{{ sleep_times | batch(3) | list }}"
- name: Task finish
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: Playbook Finished
# batch-task.yml
- ansible.builtin.command:
cmd: "sleep {{ sleep_time_val }}"
async: 10
poll: 0
loop: "{{ batched_sleep_times }}"
loop_control:
loop_var: "sleep_time_val" # instead of "item", set a custom loop var name to avoid var name conflicts
register: async_result
- name: wait for async tasks
ansible.builtin.async_status:
jid: "{{ item.ansible_job_id }}"
register: job_status
until: job_status.finished
with_items: "{{ async_result.results }}"
retries: 30
delay: 1
Output (Click to show)
TASK [Gathering Facts] *************************************************************************************************************
Sunday 23 July 2023 18:59:36 +0000 (0:00:00.013) 0:00:00.013 ***********
ok: [docker-server]
TASK [Run in batches of 3] *********************************************************************************************************
Sunday 23 July 2023 18:59:37 +0000 (0:00:00.977) 0:00:00.990 ***********
included: /workspaces/ansible/playbooks/async/batch-task.yml for docker-server => (item=[1, 2, 3])
included: /workspaces/ansible/playbooks/async/batch-task.yml for docker-server => (item=[4, 5, 6])
included: /workspaces/ansible/playbooks/async/batch-task.yml for docker-server => (item=[7])
TASK [ansible.builtin.command] *****************************************************************************************************
Sunday 23 July 2023 18:59:38 +0000 (0:00:00.106) 0:00:01.097 ***********
changed: [docker-server] => (item=1)
changed: [docker-server] => (item=2)
changed: [docker-server] => (item=3)
TASK [wait for async tasks] ********************************************************************************************************
Sunday 23 July 2023 18:59:39 +0000 (0:00:00.989) 0:00:02.087 ***********
[WARNING]: TASK: wait for async tasks: The loop variable 'item' is already in use. You should set the `loop_var` value in the
`loop_control` option for the task to something else to avoid variable collisions and unexpected behavior.
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (30 retries left).
changed: [docker-server] => (item={'failed': 0, 'started': 1, 'finished': 0, 'ansible_job_id': 'j916389662055.16043', 'results_file': '/home/user/.ansible_async/j916389662055.16043', 'changed': True, 'sleep_time_val': 1, 'ansible_loop_var': 'sleep_time_val'})
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (30 retries left).
changed: [docker-server] => (item={'failed': 0, 'started': 1, 'finished': 0, 'ansible_job_id': 'j281706512657.16093', 'results_file': '/home/user/.ansible_async/j281706512657.16093', 'changed': True, 'sleep_time_val': 2, 'ansible_loop_var': 'sleep_time_val'})
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (30 retries left).
changed: [docker-server] => (item={'failed': 0, 'started': 1, 'finished': 0, 'ansible_job_id': 'j921227415397.16133', 'results_file': '/home/user/.ansible_async/j921227415397.16133', 'changed': True, 'sleep_time_val': 3, 'ansible_loop_var': 'sleep_time_val'})
TASK [ansible.builtin.command] *****************************************************************************************************
Sunday 23 July 2023 18:59:43 +0000 (0:00:04.142) 0:00:06.229 ***********
changed: [docker-server] => (item=4)
changed: [docker-server] => (item=5)
changed: [docker-server] => (item=6)
TASK [wait for async tasks] ********************************************************************************************************
Sunday 23 July 2023 18:59:44 +0000 (0:00:00.881) 0:00:07.111 ***********
[WARNING]: TASK: wait for async tasks: The loop variable 'item' is already in use. You should set the `loop_var` value in the
`loop_control` option for the task to something else to avoid variable collisions and unexpected behavior.
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (30 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (29 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (28 retries left).
changed: [docker-server] => (item={'failed': 0, 'started': 1, 'finished': 0, 'ansible_job_id': 'j116343627294.16434', 'results_file': '/home/user/.ansible_async/j116343627294.16434', 'changed': True, 'sleep_time_val': 4, 'ansible_loop_var': 'sleep_time_val'})
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (30 retries left).
changed: [docker-server] => (item={'failed': 0, 'started': 1, 'finished': 0, 'ansible_job_id': 'j515812820963.16476', 'results_file': '/home/user/.ansible_async/j515812820963.16476', 'changed': True, 'sleep_time_val': 5, 'ansible_loop_var': 'sleep_time_val'})
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (30 retries left).
changed: [docker-server] => (item={'failed': 0, 'started': 1, 'finished': 0, 'ansible_job_id': 'j228776870178.16516', 'results_file': '/home/user/.ansible_async/j228776870178.16516', 'changed': True, 'sleep_time_val': 6, 'ansible_loop_var': 'sleep_time_val'})
TASK [ansible.builtin.command] *****************************************************************************************************
Sunday 23 July 2023 18:59:50 +0000 (0:00:06.885) 0:00:13.996 ***********
changed: [docker-server] => (item=7)
TASK [wait for async tasks] ********************************************************************************************************
Sunday 23 July 2023 18:59:51 +0000 (0:00:00.282) 0:00:14.278 ***********
[WARNING]: TASK: wait for async tasks: The loop variable 'item' is already in use. You should set the `loop_var` value in the
`loop_control` option for the task to something else to avoid variable collisions and unexpected behavior.
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (30 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (29 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (28 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (27 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (26 retries left).
FAILED - RETRYING: [docker-server]: wait for async tasks (25 retries left).
changed: [docker-server] => (item={'failed': 0, 'started': 1, 'finished': 0, 'ansible_job_id': 'j854860904354.16926', 'results_file': '/home/user/.ansible_async/j854860904354.16926', 'changed': True, 'sleep_time_val': 7, 'ansible_loop_var': 'sleep_time_val'})
TASK [Task finish] *****************************************************************************************************************
Sunday 23 July 2023 18:59:59 +0000 (0:00:08.177) 0:00:22.456 ***********
ok: [docker-server] => {
"msg": "Playbook Finished"
}
PLAY RECAP *************************************************************************************************************************
docker-server : ok=11 changed=6 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Sunday 23 July 2023 18:59:59 +0000 (0:00:00.062) 0:00:22.519 ***********
===============================================================================
wait for async tasks -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 8.17s
wait for async tasks -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6.89s
wait for async tasks -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 4.14s
ansible.builtin.command ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.99s
Gathering Facts ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.98s
ansible.builtin.command ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.88s
ansible.builtin.command ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.29s
Run in batches of 3 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.11s
Task finish ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.06sScenario: Restart a host and wait for reboot to complete
There are 2 ways to do this:
- Use the
rebootmodule (if your Ansible version has this module) - Use
shellcommand to reboot (async) the host and use thewait_formodule to wait for the reboot to complete
Method 1 - restart and wait using reboot
- hosts: dev
tasks:
- name: restart host & wait for restart to finish
ansible.builtin.reboot:
become: true
- ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "Server Restarted"
Output (Click to show)
TASK [restart host & wait for restart to finish] ****************************************************************************
Monday 24 July 2023 18:57:39 +0000 (0:00:01.384) 0:00:01.396 ***********
changed: [dev]
TASK [ansible.builtin.debug] ************************************************************************************************
Monday 24 July 2023 18:57:49 +0000 (0:00:09.606) 0:00:11.003 ***********
ok: [dev] => {
"msg": "Server Restarted"
}
PLAY RECAP ******************************************************************************************************************
dev : ok=3 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Monday 24 July 2023 18:57:49 +0000 (0:00:00.057) 0:00:11.060 ***********
===============================================================================
restart host & wait for restart to finish ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 9.61s
Gathering Facts ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 1.38s
ansible.builtin.debug ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 0.06sMethod 2 - restart and wait using shell & wait_for_connection
If you are running an older version of Ansible that does not have the reboot module, you can use the shell module for restarting the server and wait_for_connection to wait for the server to go back online.
- hosts: dev
tasks:
- name: restart host
ansible.builtin.shell:
cmd: "reboot now"
async: 1
poll: 0
become: true
- name: wait for host to restart
ansible.builtin.wait_for_connection:
delay: 10
timeout: 120
Explanation:
- restart
devserver usingshellmodule - fire-and-forget the restart task (
async: 1andpoll: 0) - make sure to run as privileged use
wait_for_connectionwill wait for our target host (dev) to be back online
Output (Click to show)
TASK [restart host] *********************************************************************************************************
Monday 24 July 2023 18:46:41 +0000 (0:00:02.509) 0:00:02.520 ***********
changed: [dev]
TASK [wait for host to restart] *********************************************************************************************
Monday 24 July 2023 18:46:42 +0000 (0:00:00.516) 0:00:03.037 ***********
ok: [dev]
PLAY RECAP ******************************************************************************************************************
dev : ok=3 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
Monday 24 July 2023 18:46:53 +0000 (0:00:10.894) 0:00:13.931 ***********
===============================================================================
wait for host to restart -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 10.89s
Gathering Facts ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 2.51s
restart host --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0.52sYou can also use wait_for instead, to wait for the host to restart by checking if port 22 (SSH) is accessible (example from Ansible docs):
# Do not assume the inventory_hostname is resolvable and delay 10 seconds at start
- name: Wait 300 seconds for port 22 to become open and contain "OpenSSH"
ansible.builtin.wait_for:
port: 22
host: '{{ (ansible_ssh_host|default(ansible_host))|default(inventory_hostname) }}'
search_regex: OpenSSH
delay: 10
connection: local
Scenario: retry async task inside block after resuce task
Since you cannot use retries with a block task, you will need to use some work around to achieve “retries” in a block task that uses async actions.
See this example, but replace the block task to your async task.
Conclusion
As always, if you’ve managed to read this far, then I hope you’ve found this article helpful! Using asynchronous actions with your playbook will make your playbooks more efficient and can speed up your playbooks!
But do remember to always be aware of any potential conflicts you may run into when running some tasks concurrently (e.g. 2 tasks might be trying to access the same file at the same time).
Also, for more tips and tricks on parallelization of your ansible playbooks check out this other article since asynchronous actions are not the only way to speed up and improve your playbook’s efficiency!
