Table of Contents
Sometimes if you’re like me, you need to run code in a remote server, may it be for security reasons, or just that the services your code uses is in a remote server.
Thankfully it’s quite easy to do local and remote sync in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) thanks to the SFTP plugin:
Prerequisites
- VSCode
- SSH connection to a remote server
1. Download and Install the SFTP extension
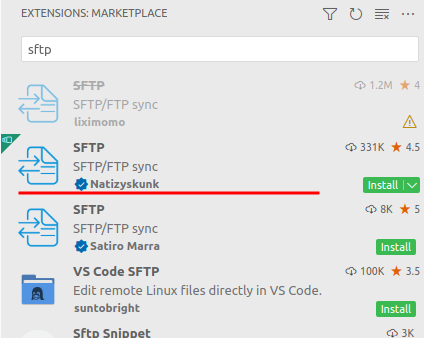
There are quite a few sftp extensions, but this version by @Natizyskunk was the one I found the most convenient to use.
2. Setup the SFTP configs for your project
- Open your project on VScode
- Press
Ctrl+Shift+PORF1 - Type
SFTPand select “SFTP:config”
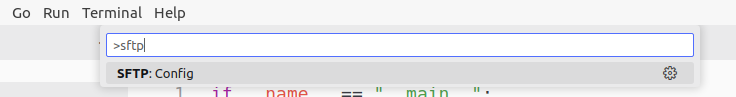
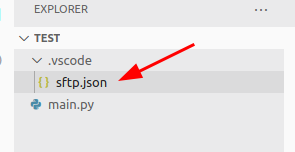
This will create a sftp.json file inside your project. This will contain the settings of your sftp connection for your specific project. This means that you will have a different sftp connection for each project!
Fill in the config details, usually the default config fields is enough, and you just need to change the values. Then save your changes.
// sftp.json
{
"name": "test-server", // name of your server
"host": "192.168.0.250", // host url/ip of your remote server
"protocol": "sftp",
"port": 22,
"username": "user", // username to access remote server
"remotePath": "/home/user/dev", // where you want the project saved in the remote server
"uploadOnSave": true,
"useTempFile": false,
"openSsh": true
}
For others who have SSH configs setup for authentication to your remote server, you can use the privateKeyPath field to provide a path to your private key from your local machine
3. Sync between local and remote server
After you’ve saved your configs, the SFTP icon on the side-bar should pop up AND when you press Ctrl+Shift+P OR F1 you’ll have access to a whole host of options

For me its just these 3 options that I need and that’s it.
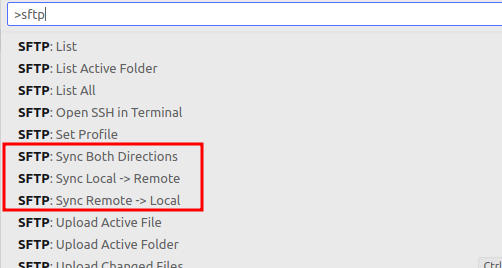
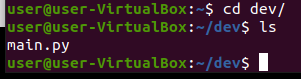
Now we check that the files have been synced to the remote server:
Potential Issues you might run into
- Permission Denied error: If you run into permission denied errors, make sure to check your remotePath in the
sftp.jsonand make sure it’s a folder that your username access has write access to. I made the classic mistake of setting remotePath to /dev when I needed root access to do that. - SSH authentication error: Make sure to specify the agent, and sshConfigPath and also privateKeyPath (unless the private key is already specified in your ssh config file)
- Deleted File changes not being reflected automatically - This can be quite a dangerous feature, but if you’re happy with files being auto deleted on your remote then the
watcher.autoDeletewill do the trick